67 - 13
2 * 4
268 / 43SQM tutorial - Week 1
Why R?
R can be used to analyse all sorts of data, from tabular data (also known as “spreadsheets”), textual data, geographic data and even images.
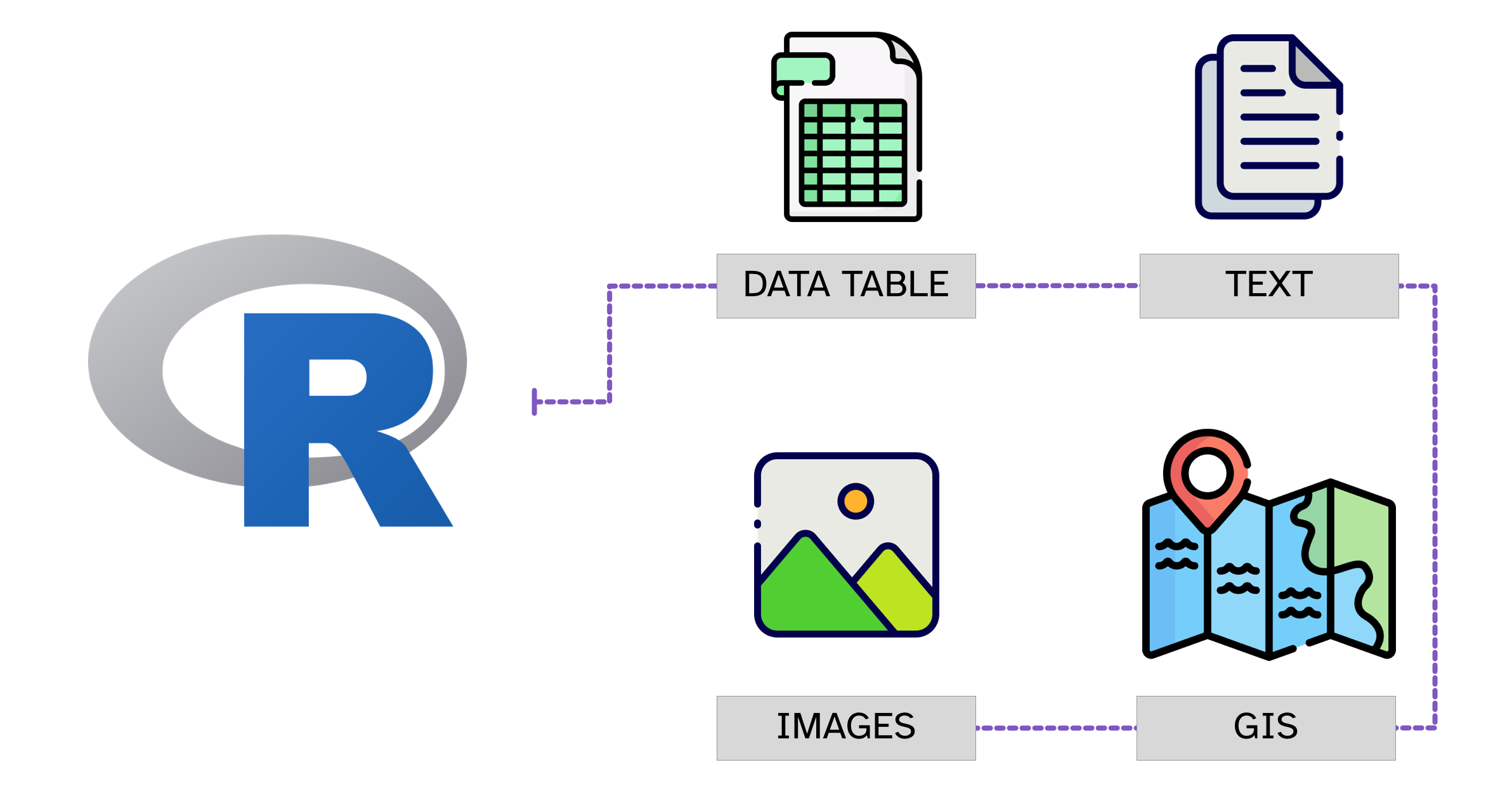
This course will focus on the analysis of tabular data, since all of the techniques relevant to this type of data also apply to the other types.

The R community is a very inclusive community and it’s easy to find help. There are several groups that promote R in minority/minoritised groups, like R-Ladies, Africa R, and Rainbow R just to mention a few.
Moreover, R is open source and free!
R vs RStudio
Beginners usually have trouble understanding the difference between R and RStudio.
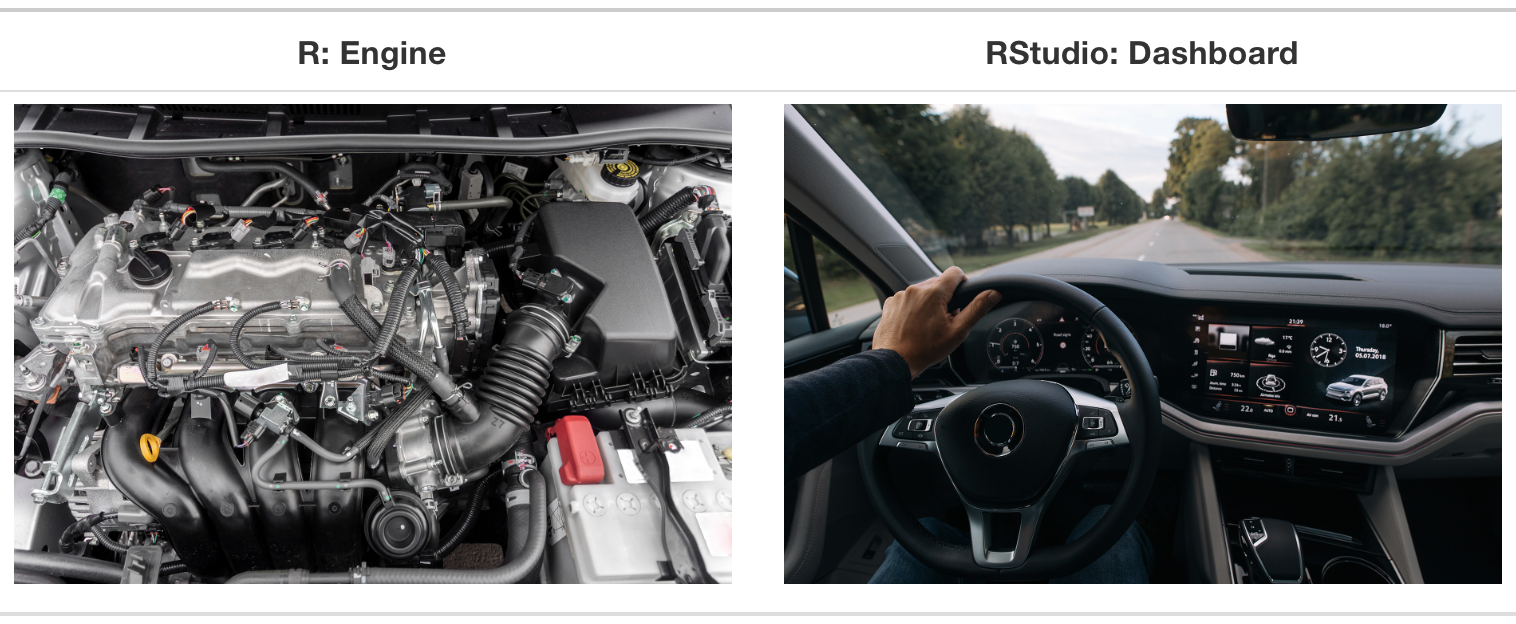
Let’s use a car analogy.
What makes the car go is the engine and you can control the engine through the dashboard.
You can think of R as an engine and RStudio as the dashboard.
The next section will give you a tour of RStudio.
RStudio
When you open RStudio, you can see the window is divided into 3 panels:
Blue (left): the Console.
Green (top-right): the Environment tab.
Purple (bottom-right): the Files tab.
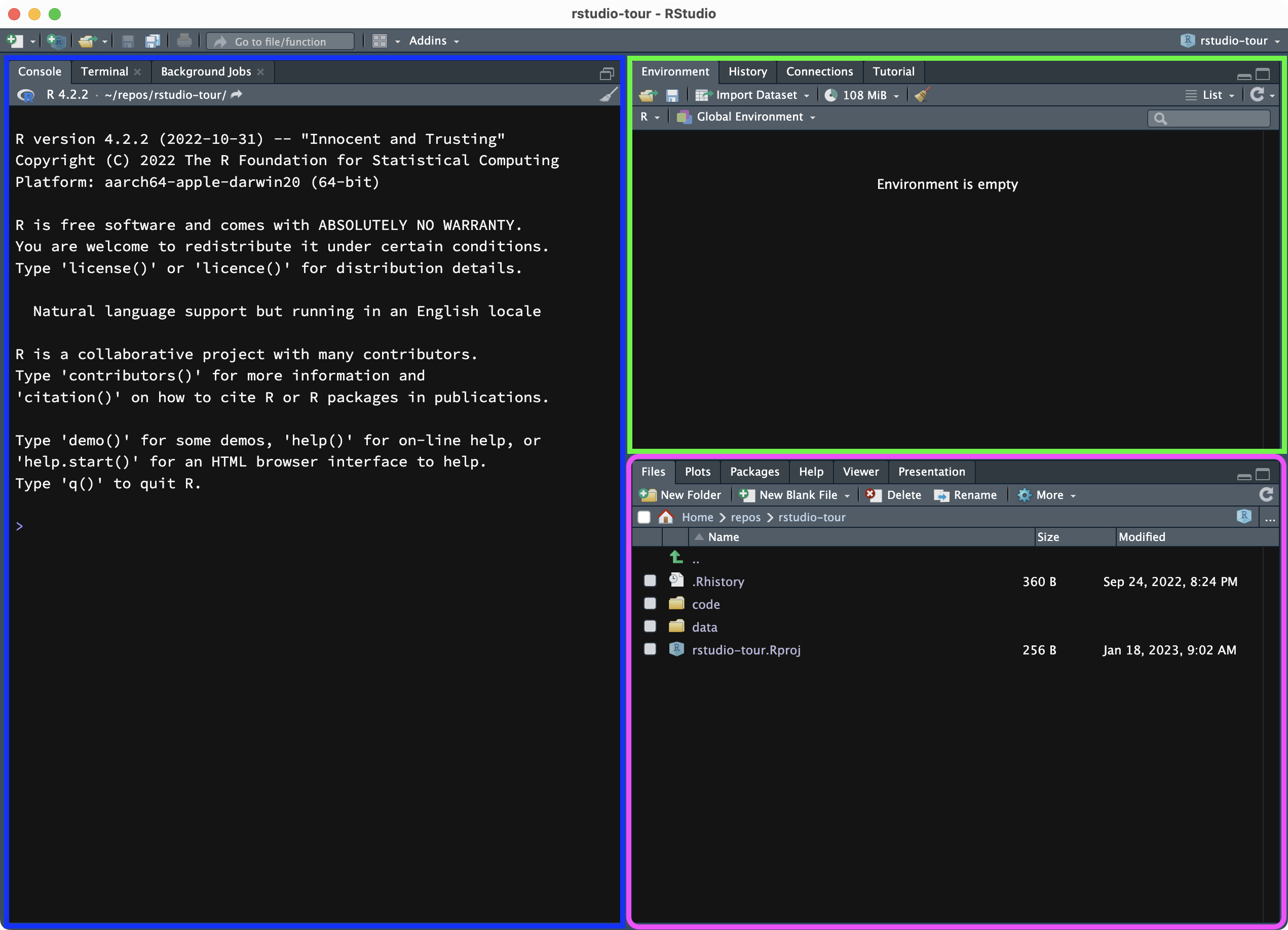
The Console is where R commands can be executed. Think of this as the interface to R.
The Environment tab lists the objects created with R, while in the Files tab you can navigate folders on your computer to get to files and open them in the file Editor.
RStudio projects
RStudio is an IDE (see above) which allows you to work efficiently with R, all in one place.
Note that files and data live in folders on your computer, outside of RStudio: do not think of RStudio as an app where you can save files in.
All the files that you see in the Files tab are files on your computer and you can access them from the Finder or File Explorer as you would with any other file.
In principle, you can open RStudio and then navigate to any folder or file on your computer.
However, there is a more efficient way of working with RStudio: RStudio Projects.
You can create as many RStudio Projects as you wish, and I recommend to create one per project (your dissertation, a research project, etc…).
We will create an RStudio Project for this course. You will be using this Project throughout the semester.
To create an RStudio Project, click on the button that looks like a transparent light blue box with a plus, in the top-left corner of RStudio. A window like the one below will pop up.
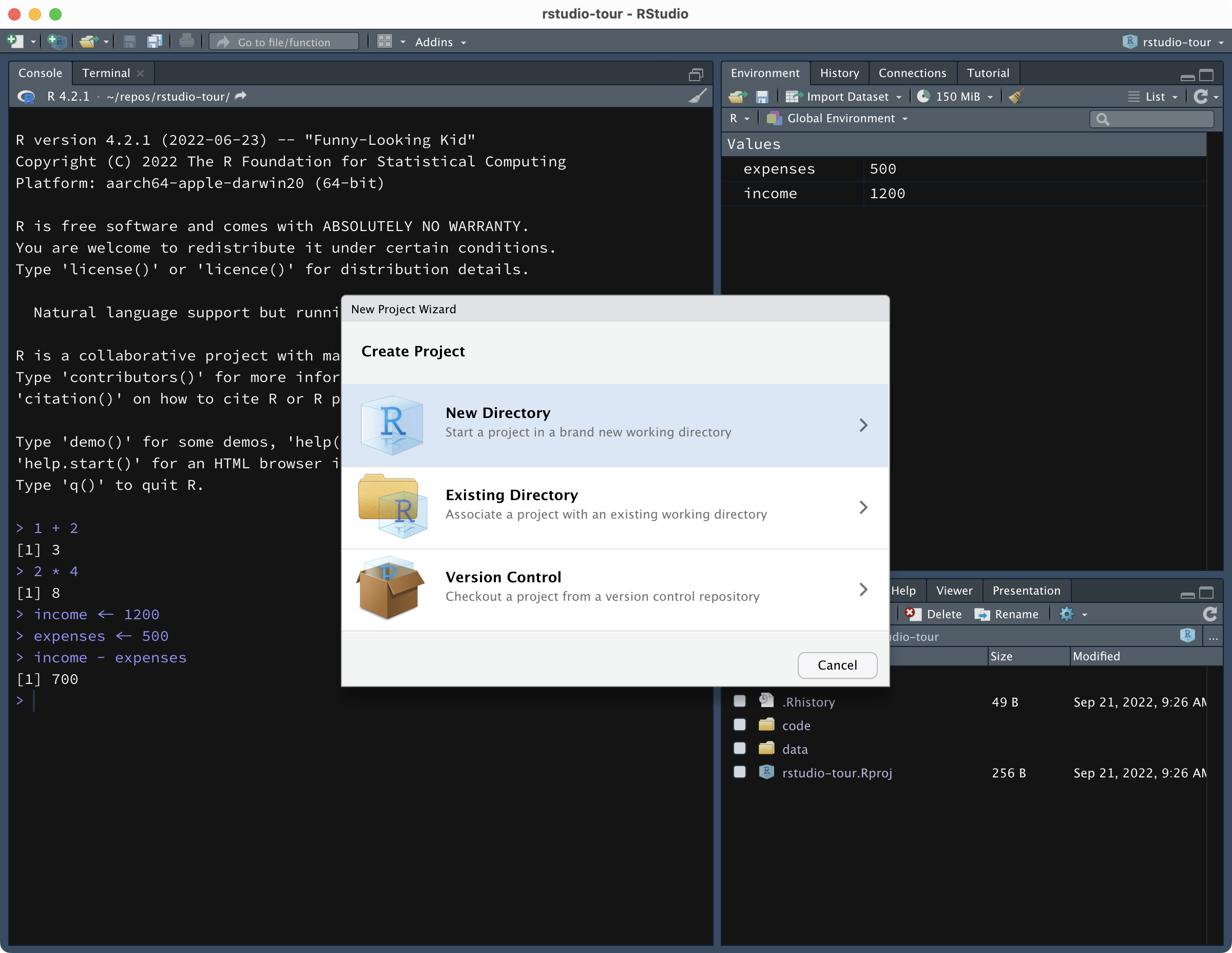
Click on New Directory then New Project.
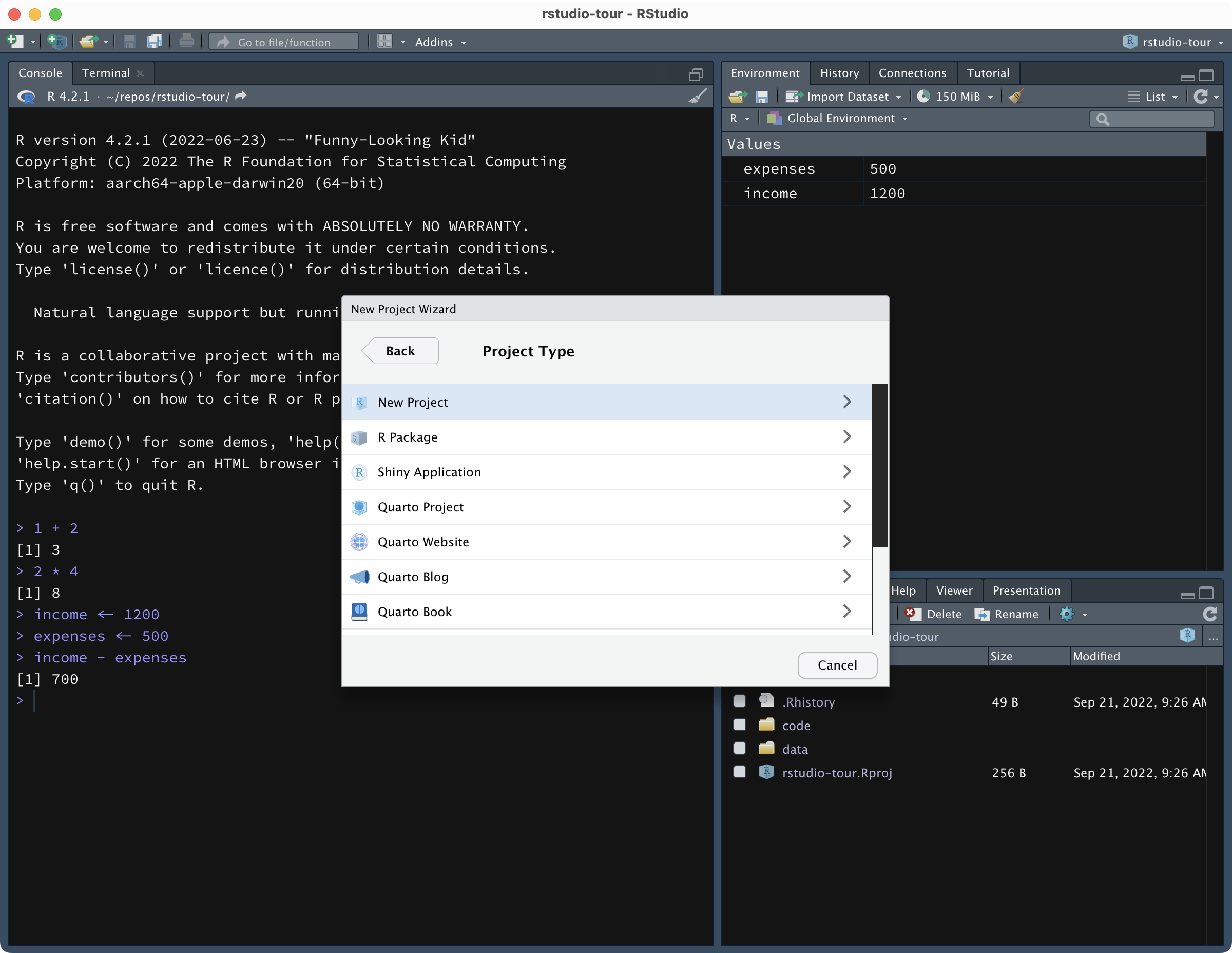
Now, this will create a new folder (aka directory) on your computer and will make that an RStudio Project.
Give a name to your new project, something like the name of the course and year.
Then you need to specify where to create this new folder/Project. Click on Browse… and navigate to the folder you want to create the new folder/Project in.
When done, click on Create Project. RStudio will automatically open your new project.
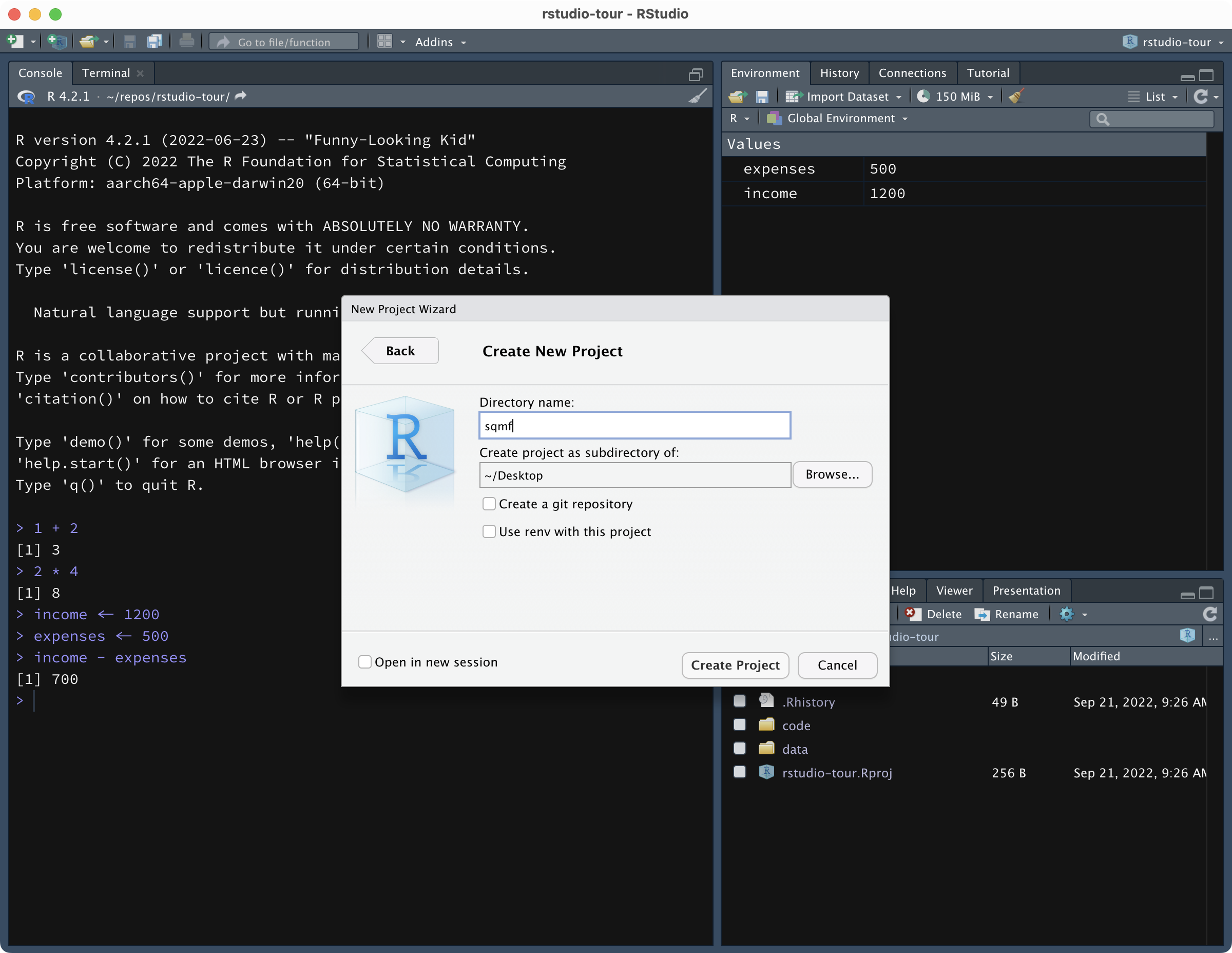
You know you are in an RStudio Project because you can see the name of the Project in the top-right corner of RStudio.
If your see Project (none) in the top-right corner, that means your are not in an RStudio Project.
There are several ways of opening an RStudio Project:
You can go to the RStudio Project folder in Finder or File Explorer and double click on the
Rprojfile.You can click on
File > Open Projectin the RStudio menu.You can click on the project name in the top-right corner of RStudio, which will bring up a list of projects. Click on the desired project to open it.
A few important settings
Before moving on, there are a few important settings that you need to change.
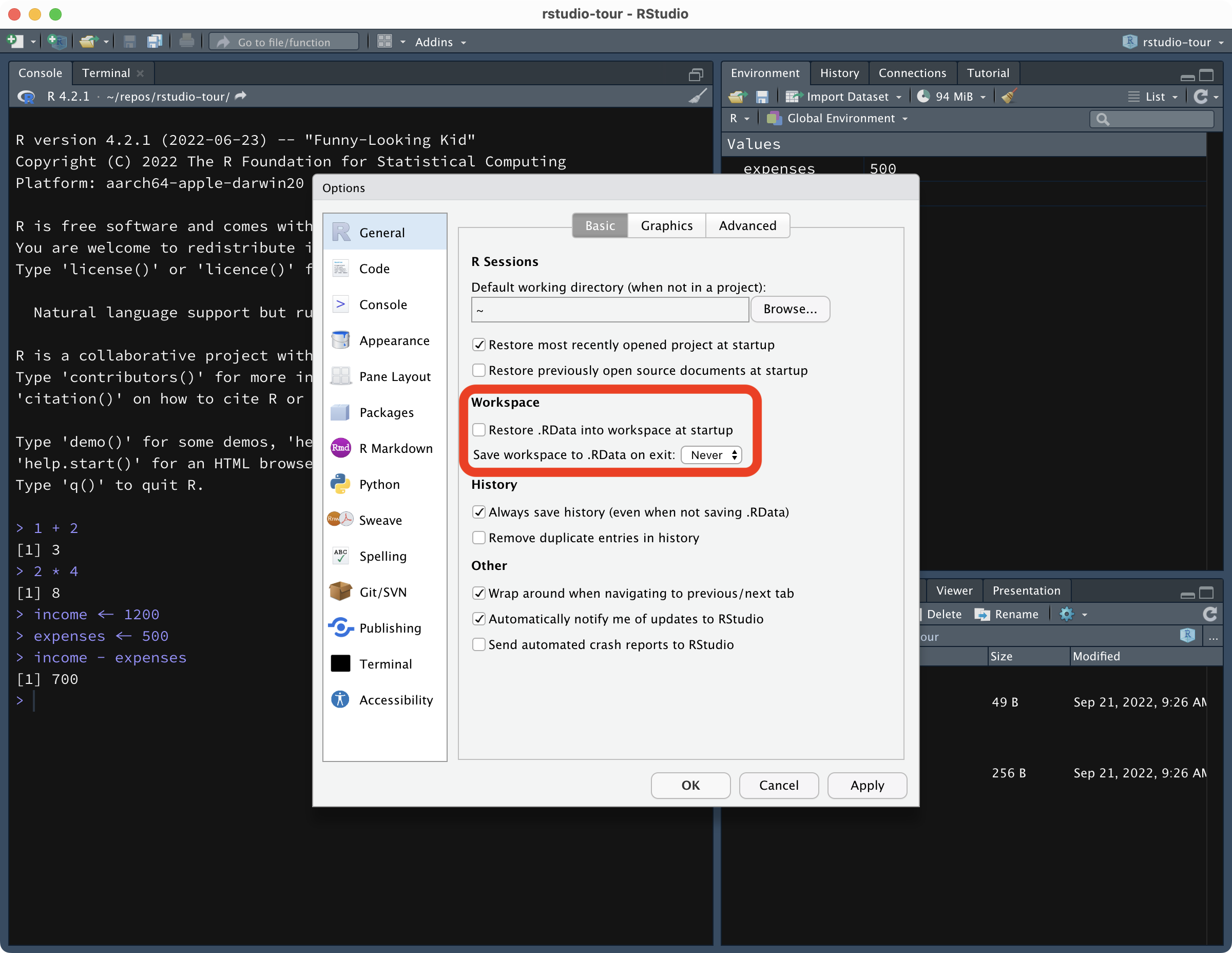
Open the RStudio preferences (
Tools > Global options...).Un-tick
Restore .RData into workspace at startup.Select
NeverinSave workspace to .RData on exit.Click
OKto confirm the changes.
R basics
R as a calculator
Write the following in the Console, then press ENTER: 1 + 2.
Fantastic! You should see that the answer to the addition has been printed in the Console, like this:
[1] 3Now, try some more operations (write each of the following in the Console and press ENTER). Feel free to add your own to the mix!
You can also chain multiple operations.
6 + 4 - 1 + 2
4 * 2 + 3 * 2Variables
Forget-me-not.
Most times, we want to store a certain value so that we can use it again later.
We can achieve this by creating variables.
You can create a variable by using the assignment operator <-.
Let’s assign the value 156 to the variable my_num.
my_num <- 156Now, check the list of variables in the Environment tab of the top-right panel of RStudio. You should see the my_num variable and its value there.
Now, you can just call the variable back when you need it! Write the following in the Console and press ENTER.
my_num[1] 156A variable like my_num is also called a numeric vector: i.e. a vector that contains a number (hence numeric).
Let’s now try some operations using variables.
income <- 1200
expenses <- 500
income - expenses[1] 700See? You can use operations with variables too!
And you can also go all the way with variables.
savings <- income - expensesAnd check the value…
savings[1] 700Vectors can hold more than one item or value.
Just use the combine c() function to create a vector containing multiple values.
The following are all numeric vectors.
one_i <- 6
# Vector with 2 values
two_i <- c(6, 8)
# Vector with 3 values
three_i <- c(6, 8, 42)Check the list of variables in the Environment tab. You will see now that before the values of two_i and three_i you get the vector type num for numeric. (If the vector has only one value, you don’t see the type in the Enviroment list but it is still of a particular type).
Note that the following are the same:
one_i <- 6
one_i[1] 6one_ii <- c(6)
one_ii[1] 6Functions
R cannot function without… functions.
A function in R has the form function() where:
functionis the name of the function, likesum.()are round parentheses, inside of which you write arguments, separated by commas.
Let’s see an example:
sum(3, 5)[1] 8The sum() function sums the number listed as arguments. Above, the arguments are 3 and 5.
And of course arguments can be vectors!
my_nums <- c(3, 5, 7)
sum(my_nums)[1] 15mean(my_nums)[1] 5String and logical vectors
Not just numbers.
We have seen that variables can hold numeric vectors. But vectors are not restricted to being numeric. They can also store strings.
A string is basically a set of characters (a word, a sentence, a full text).
In R, strings have to be quoted using double quotes " ".
Change the following strings to your name and surname. Remember to keep the double quotes
name <- "Stefano"
surname <- "Coretta"
name[1] "Stefano"Strings can be used as arguments in functions, like numbers can.
cat("My name is", name, surname)My name is Stefano CorettaRemember that you can reuse the same variable name to override the variable value.
name <- "Raj"
cat("My name is", name, surname)My name is Raj CorettaYou can combine multiple strings into a character vector, using c().
fruit <- c("apple", "oranges", "bananas")
fruit[1] "apple" "oranges" "bananas"Check the Environment tab. Character vectors have chr before the values.
Another type of vector is one that contains either TRUE or FALSE. Vectors of this type are called logical vectors and they are listed as logi in the Environment tab.
groceries <- c("apple", "flour", "margarine", "sugar")
in_pantry <- c(TRUE, TRUE, FALSE, TRUE)TRUE and FALSE values must be written in all capitals and without double quotes (they are not strings!).